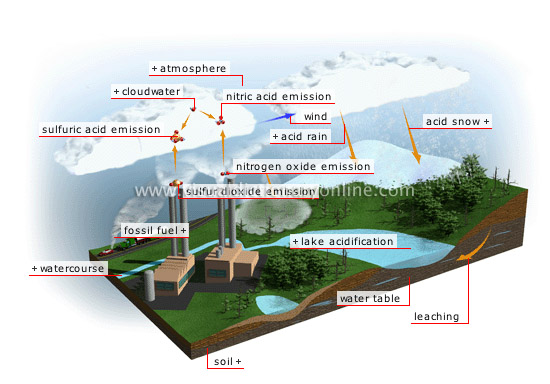
acid rain
Rain that contains abnormally high concentrations of sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
sulfuric acid emission 
Sulfuric acid forms when sulfur dioxide combines with cloudwater.
sulfur dioxide emission 
Sulfur dioxide is produced mainly by coal-fired thermal power plants and smelters that refine ores with high sulfur content.
fossil fuel 
The use of fossil fuels by motor vehicles and industry triggers emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
watercourse 
Natural flow of water that varies in volume, depending on the ground slope and the number of tributaries.
soil 
Surface layer of the Earth’s crust; it results from the alteration of bedrock and the decomposition of organic matter.
water table 
Vast expanse of underground water fed by rainwater filtering through the earth; it supplies springs and can be collected in wells.
lake acidification 
It causes plankton depletion and creates an imbalance in the food chain, sometimes leading to the total disappearance of plant and animal life.
leaching 
Acid rain robs the soil of nutrients that are indispensable to plant life, such as magnesium, calcium and potassium.
acid snow 
Acid rain can take the form of snowflakes and fog.
wind 
Polluted clouds are carried by the wind, sometimes traveling thousands of miles; their pollutants then fall in the form of acid rain.
acid rain 
Rain that contains abnormally high concentrations of sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
atmosphere 
Layer of air that surrounds the Earth and is composed mainly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%); only its lower portion is part of the biosphere.
nitrogen oxide emission 
Nitrogen oxide is discharged by motor vehicles and thermal power plants that burn fossil fuels.
cloudwater 
Nitric acid and sulfuric acid dissolve in cloudwater.
nitric acid emission 
Nitric acid forms when nitrogen oxides combine with cloudwater.