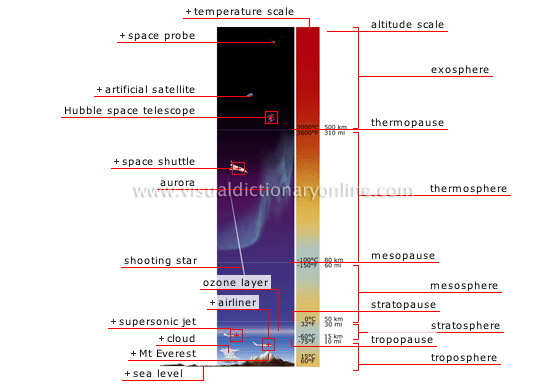
profile of the Earth’s atmosphere
Atmosphere: layer of air that surrounds the Earth and is composed mainly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%); its density decreases with altitude.
space probe 
Unmanned craft launched in the direction of a celestial body in the solar system for purposes of studying it.
artificial satellite 
Observation spacecraft placed in orbit around the Earth.
space shuttle 
It orbits at an altitude of about 250 mi.
aurora 
Luminous phenomenon that occurs at high altitudes near the Earth’s poles.
shooting star 
Luminous trace produced when a meteorite burns up as it enters the Earth’s atmosphere.
airliner 
Commercial aircraft that makes regular flights of variable duration, depending on the distance covered; it flies at altitudes of 39,000 feet.
ozone layer 
Layer of gas that absorbs a large part of the Sun’s ultraviolet rays.
Mt Everest 
The world’s highest peak rises to an elevation of 29,035 feet.
supersonic jet 
Aircraft whose cruising speed is faster than the speed of sound; it flies at altitudes of 62,000 feet.
cloud 
Fine droplets of water or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere.
sea level 
Average height of seawater observed for a given time (day, month, year); it is used as a reference point to define coastal features and measure land elevations.
troposphere 
The most dense layer, which produces most of the meteorological phenomena and where temperatures decrease with altitude.
stratosphere 
Highly stable layer of air where temperatures increase with altitude due to the absorption of solar radiation by the ozone layer.
tropopause 
The boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere; its altitude varies depending on the season, ground temperature, latitude and atmospheric pressure.
stratopause 
Thin transition layer between the stratosphere and the mesosphere.
mesosphere 
The atmosphere’s coldest layer, where temperatures decrease with altitude.
mesopause 
Thin transition layer between the mesosphere and the thermosphere.
thermosphere 
Layer that absorbs a large portion of solar radiation, leading to a steady increase in its temperature.
thermopause 
Thin transition layer between the thermosphere and the exosphere.
exosphere 
The outermost region of the atmosphere, where low-density gases disperse into space.
temperature scale 
altitude scale 
Hubble space telescope 
Telescope placed in orbit above Earth’s atmosphere (370 mi), making it possible to observe the universe as never before.