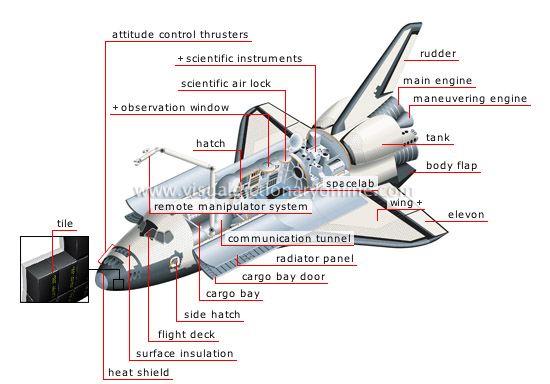
orbiter
The only part of the shuttle to fly in orbit; can transport 13 tons of material and five to seven astronauts.
side hatch 
Door allowing the crew to embark and disembark before the launch and after the return to Earth.
heat shield 
Protects the orbiter nose from heat caused by friction when the vehicle enters the atmosphere; covered with carbon fiber, it can withstand temperatures over 2,900°F.
attitude control thrusters 
Small rocket engines that direct the orbiter to the desired position.
surface insulation 
Protects against heat so that the orbiter does not burn up on re-entry into the atmosphere.
flight deck 
Forward section of the orbiter housing the crew, flight-control equipment and monitor.
cargo bay 
Shuttle compartment that stores various types of cargo, depending on the mission (satellite, probe, laboratory, telescope).
remote manipulator system 
Mechanical arm used to handle and move shuttle cargo.
radiator panel 
Discharges into space the heat produced by the functioning of onboard equipment.
cargo bay door 
Remains open in orbit so as to expose the content of the cargo bay to space.
hatch 
Opening that provides access to the communications tunnel.
spacelab 
Area where scientific experiments on weightlessness are carried out.
wing 
Horizontal surface acted on by aerodynamic forces that keep the orbiter aloft in the atmosphere.
elevon 
Each of the two ailerons controls pitching during landing.
body flap 
Part serving as a thermal shield for the motors during re-entry into the atmosphere.
tank 
Contains fuel for the maneuvering engines and the directional control thrusters.
main engine 
Each of the orbiter’s three tail engines used during takeoff; these only function for the first 8 min. of flight.
maneuvering engine 
Used to place the vehicle in orbit, to provide thrust in case the orbit changes and to take the vehicle out of orbit.
rudder 
Mobile vertical part that allows the orbiter to set its direction when landing.
scientific instruments 
Varying for each mission, they make it possible, for example, to study meteorological conditions, pollution and cosmic radiation.
scientific air lock 
Door making it possible to expose equipment to the space vacuum.
communication tunnel 
Corridor that allows the astronauts to go from the orbiter crew compartment to the laboratory.
observation window 
Window that makes it possible to see outside the orbiter.
tile 
Covering 70% of the orbiter, the tiles protect it from heat on re-entry into the atmosphere.