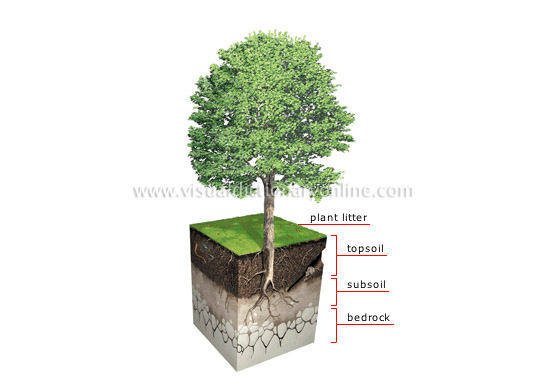
soil profile
Soil usually has four main layers; it varies in total thickness from several inches to several feet, depending on the area.
bedrock 
Rock that forms the bottom layer of soil; its physical and chemical breakdown enables the upper layers to develop.
subsoil 
Third layer of soil to which the roots extend; contains little organic matter but many nutrients leached from the topsoil.
plant litter 
Upper layer of soil, composed of recently fallen animal and vegetable scraps or those in the early stages of decomposition.
topsoil 
Second layer of soil, dark in color and rich in organic matter; it contains almost all of the soil’s animal and vegetable life.