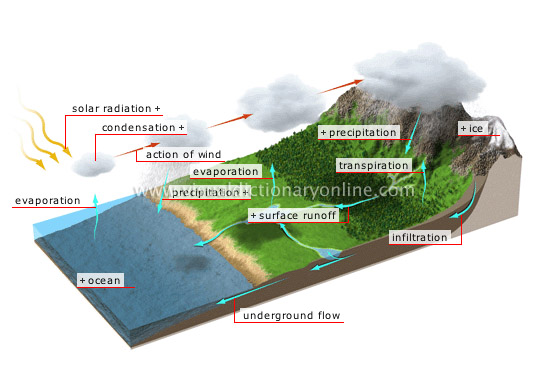
hydrologic cycle
Continuous circulation of water in its different states (liquid, solid and gaseous) between the oceans, the atmosphere and the Earth’s surface.
solar radiation 
It provides the heat necessary for water to evaporate.
condensation 
The process by which water vapor is converted, by means of cooling, into liquid or solid water in the form of clouds.
action of wind 
Driven by winds, clouds fly over the land.
ice 
Water that accumulates high in the mountains in solid form.
underground flow 
Movement of infiltrated water that joins a watercourse on the surface or flows directly into lakes or the ocean.
ocean 
Vast body of saltwater covering a large part of the Earth’s surface and separating the continents.
precipitation 
Various forms of water that fall from the atmosphere.
evaporation 
Conversion, without boiling, of liquid water into water vapor when exposed to heat.
transpiration 
Phenomenon by which plants discharge water vapor into the atmosphere.
infiltration 
Water penetrating into the soil through permeable rock.
surface runoff 
Flow of rainwater or melting snow on the surface of the ground; it produces watercourses.
evaporation 
Conversion, without boiling, of liquid water into water vapor when exposed to heat.
precipitation 
Various forms of water that fall from the atmosphere.