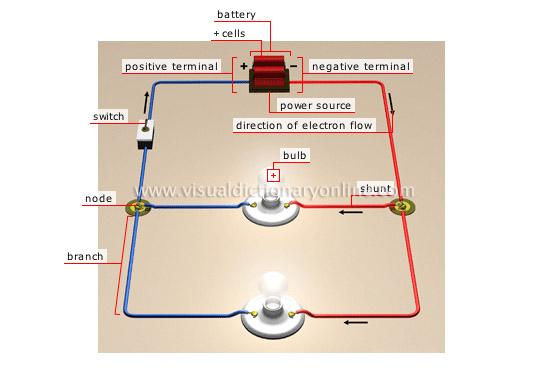
parallel electrical circuit
It is divided into independent branches, through which the current flows with partial intensity (in a series circuit, all the elements receive the same intensity).
branch 
Part of the circuit between two consecutive nodes; it constitutes an independent electric circuit.
negative terminal 
Polarity element of the battery from which the current flows through the circuit.
positive terminal 
Polarity element of the battery toward which the current flows through the circuit.
direction of electron flow 
Electrons move from the negative terminal toward the positive terminal; this is opposite to the conventional direction of the current, which flows from the positive toward the negative.
node 
Junction point of two or more branches in the electric circuit.
shunt 
It enables each device to have its own circuit and to function independently. This way, if one lightbulb does not function, the current continues to flow in the rest of the circuit.
bulb 
Gas sealed in a glass envelope into which the luminous body of a lamp is inserted.
cells 
Devices that transform chemical energy into electric energy in order to power electric devices (here, a lightbulb).
battery 
Device composed of one or more interrelated cells; each one accumulates a reserve of electricity whose purpose is to supply electricity to the circuit.
power source 
The current leaves the battery by the negative terminal, flows through the circuit to power the lightbulbs and returns to the battery by the positive terminal.
switch 
Mechanism allowing the current in an electric circuit to be established or interrupted.