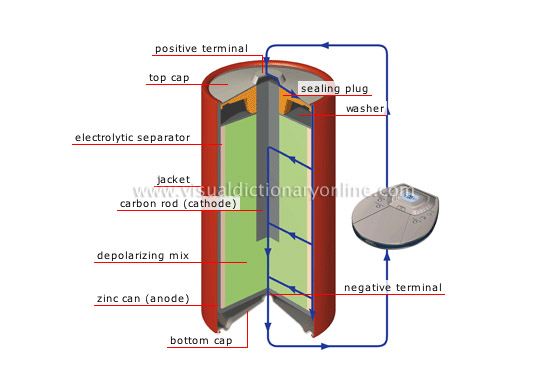
carbon-zinc cell
Battery that produces 1.5 V (also called Leclanché); its use is very widespread (pocket calculators, portable radios, alarm clocks).
washer 
Disk that compresses the depolarizing mix.
sealing plug 
Material that seals the battery.
positive terminal 
Polarity element of the battery from which the current flows.
top cap 
Upper metal cover; the positive terminal is located at its center.
electrolytic separator 
Porous paper combined with a chemical paste (ammonium chloride) that separates the two electrodes; this allows electrons to pass, thus conducting electricity.
jacket 
Battery’s protective plastic casing.
carbon rod (cathode) 
Carbon rod set in the depolarizing mix; it constitutes the battery’s negative electrode (cathode) collecting the electrons returning from the circuit.
depolarizing mix 
Mixture of carbon and manganese dioxide that augments conductivity by acting as a barrier to polarization.
zinc can (anode) 
Zinc receptacle that constitutes the battery’s positive electrode (anode).
bottom cap 
Lower metal cover; the negative terminal is located at its center.
negative terminal 
Polarity element of the battery toward which the current flows.