magnetism
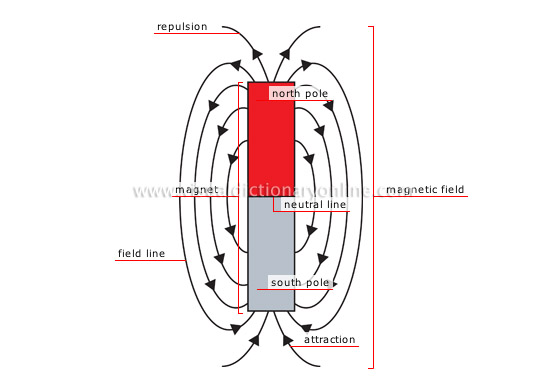
Action exerted by magnets and magnetic fields and phenomena. Magnetism can be characterized by the forces of attraction and repulsion between two masses.
attraction 
Force by which two bodies are pulled toward each other; opposite poles attract each other.
magnetic field 
Area around the magnet where magnetic forces represented by lines of force are exerted, resulting in electron movement.
neutral line 
Line separating the north and south lines of the magnet and exhibiting no magnetic phenomena.
south pole 
End of the magnet to which the field lines are directed and around which the exterior magnetic action is intense.
field line 
Imaginary line representing the direction of the magnetic forces between the north and south poles.
magnet 
Body producing an exterior magnetic field; it attracts iron, nickel and cobalt as well as their alloys.
north pole 
End of the magnet from which field lines originate and around which the exterior magnetic action is intense.
repulsion 
Force by which two bodies push against each other. Two poles of the same orientation (both positive or both negative) repulse each other.