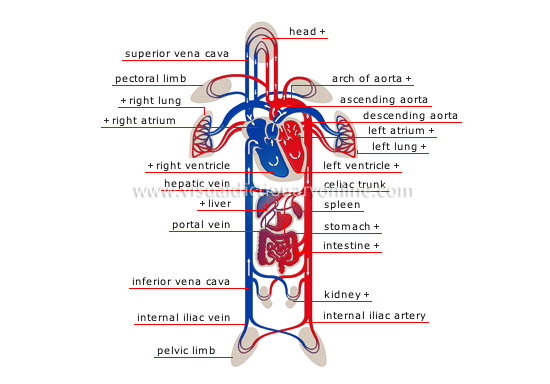
schema of circulation
Propelled by the heart, blood circulates through the body by two distinct routes: through the lungs (where it collects oxygen) and through the rest of the body.
internal iliac artery 
Branch of the aorta supplying blood to the pelvis and lower limbs; it divides into the internal and external iliac arteries.
kidney 
Organ secreting urine; it eliminates toxic substances from the body.
intestine 
Section of the digestive tract between the stomach and the anus where absorption of nutrients is carried out and waste is transformed into fecal matter.
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract preceding the intestine; it receives food to be digested.
spleen 
Organ of the circulatory system where impurities in the blood are destroyed.
celiac trunk 
Large branch of the descending aorta dividing into three arteries that flow to various abdominal organs (stomach, gallbladder, liver, pancreas).
liver 
Viscera that secretes bile, among other substances; bile helps digestion.
portal vein 
Large vein carrying blood from the abdominal organs (small intestine, stomach, gallbladder, pancreas and others) to the liver.
inferior vena cava 
Vein carrying blood deoxygenated in the lower portion of the body (below the diaphragm) to the right atrium; it is the largest vein in the organism.
internal iliac vein 
Vein carrying blood from the lower limb back to the inferior vena cava.
pelvic limb 
Attached to the trunk at the hip, it is made up of the thigh, the leg and the foot; its role is to support the body.
pectoral limb 
Attached to the trunk at the shoulder, it is made up of the arm, the forearm and the hand.
left ventricle 
Thick-walled heart cavity receiving oxygenated blood from the left atrium; it then forces it into the aorta to circulate throughout the organism.
left atrium 
Heart cavity receiving oxygenated blood from the lungs via four pulmonary veins; it then forces it into the left ventricle.
left lung 
Respiratory organ divided into two lobes where blood from the pulmonary artery is cleansed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen.
descending aorta 
Third segment of the aorta flowing down the thorax to the diaphragm; it then branches into various arteries between the ribs.
arch of aorta 
Second segment of the aorta, which branches into the arteries flowing to the head and upper limbs; with the ascending aorta, it forms the arch of the aorta.
ascending aorta 
First segment of the artery leaving from the left ventricle; it branches into two coronary arteries that flow to the heart.
head 
Upper portion of the body containing the main sensory organs and the brain.
hepatic vein 
Vein carrying blood from the liver back to the inferior vena cava.
right ventricle 
Thin-walled heart cavity receiving deoxygenated blood from the right atrium; it then forces it into the pulmonary artery leading to the lungs.
right atrium 
Heart cavity receiving deoxygenated blood from the lower and upper venae cavae; it then forces it into the right ventricle.
right lung 
Respiratory organ divided into three lobes in which blood from the pulmonary artery is cleansed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen.
superior vena cava 
Vein carrying deoxygenated blood from the upper body (above the diaphragm) back to the right atrium.