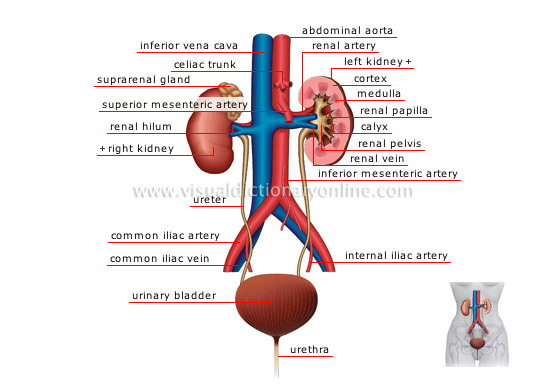
urinary system
Eliminates the organism’s waste through secretion and evacuation of urine; it also regulates the quantity of water and salt in the body.
suprarenal gland 
Organ situated atop the kidney, not part of the urinary system; it secretes various hormones of the steroid and adrenal families.
celiac trunk 
Large branch of the descending aorta dividing into three arteries that flow to various abdominal organs (stomach, gallbladder, liver, pancreas).
cortex 
Outer portion of the renal tissue inserted between the Malpighian pyramids; it is made up of small vesicles that filter the blood and produce urine.
left kidney 
Organ located beneath the gallbladder; it filters the blood and secretes urine to eliminate toxic substances and waste from the body.
medulla 
Inner part of the renal tissue made up of Malpighian pyramids, cone-shaped structures that connect the urine collection canals.
renal papilla 
Crest of the Malpighian pyramid (cone-shaped striated structure) made of urine collection canals; it opens into the calyx.
calyx 
Excretory cavity of the kidney; it collects urine flowing from the papillae and opens into the renal pelvis.
renal pelvis 
Broad section of the excretory renal tract resulting from the juncture of the calyxes; it extends into the ureter.
renal vein 
Large vein collecting blood from the kidney; it flows into the inferior vena cava.
renal artery 
Branch of the abdominal aorta circulating blood to the kidney.
superior mesenteric artery 
Branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the ascending colon and half of the transverse colon.
inferior mesenteric artery 
Branch of the abdominal aorta circulating blood to the descending colon and half the transverse colon.
urethra 
Membranous canal enabling the evacuation of urine. In the male, it also allows sperm to pass.
urinary bladder 
Muscular reservoir where urine from the kidneys collects before being evacuated through the urethra.
internal iliac artery 
Branch of the common iliac artery flowing to the pelvis, the genital organs and the inner thigh.
common iliac vein 
Vein carrying blood from the lower limb back to the inferior vena cava.
common iliac artery 
Branch of the abdominal aorta that circulates blood to the pelvis and the lower limbs; it divides into the internal and external iliac arteries.
ureter 
Long muscular membranous canal extending from the renal pelvis; it carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
abdominal aorta 
Fourth segment of the aorta circulating to all the organs and to the walls of the abdomen; it branches into the common iliac arteries.
right kidney 
Organ located beneath the liver; it filters the blood and secretes urine to eliminate toxic substances and waste from the body.
renal hilum 
Opening of the inner edge of the kidney allowing the passage of blood vessels, nerves and the ureter.
inferior vena cava 
Vein carrying blood deoxygenated in the lower portion of the body (below the diaphragm) to the right atrium; it is the largest vein in the organism.