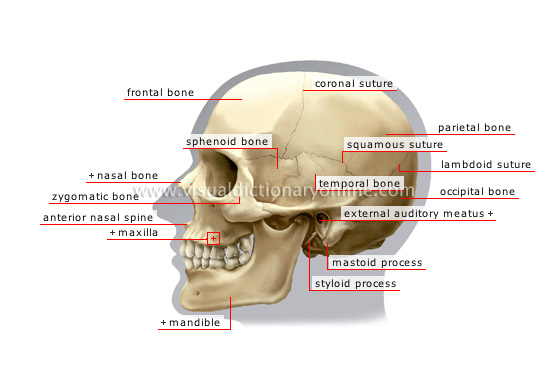
lateral view of skull
Skull: bony structure enclosing and protecting the brain. The eight cranial bones in an adult are fused to each other by means of sutures.
temporal bone 
Flat skull bone that protects mainly the organs responsible for hearing and equilibrium.
frontal bone 
Flat skull bone forming the forehead and top of the eye sockets, and articulating especially with the parietal.
zygomatic bone 
Bone forming the cheek pouch and the outer edge of the eye socket.
maxilla 
Toothed bone forming the upper jaw; it helps to form the palate, eye sockets and nasal fossae.
mandible 
Movable toothed bone forming the lower jaw; it is the only movable bone in the head and its articulation with the temporal bone allows the jaw to move.
occipital bone 
Flat skull bone articulating with the parietal bone and atlas (first cervical vertebra), among others; it makes up the largest portion of the base of the skull.
parietal bone 
Flat cranial bone articulating with the frontal, occipital, temporal and sphenoid bones; the two parietal bones form the largest portion of the dome of the skull.
lambdoid suture 
Immovable joint made of fibrous tissue connecting the occipital and the two parietal bones.
external auditory meatus 
Canal through which sounds collected by the auricle (outer section of the ear) reach the tympanic cavity, a hollow in the temporal bone.
mastoid process 
Protruding cone-shaped part of the temporal bone located behind the outer ear. Certain neck muscles, such as the sternocleidomatoid, are attached to it.
styloid process 
Elongated protuberance of the temporal bone; several tongue muscles are attached to it.
anterior nasal spine 
Bony middle protuberance of the jawbone beneath the nasal fossae; it supports the cartilage of the dividing wall of the nose.
nasal bone 
Small flat bone making up the skeleton of the nose; the two nasal bones are joined along the bridge of the nose.
sphenoid bone 
Bone located behind the nasal fossae; it articulates with all the cranial bones.
squamous suture 
Immobile joint made of fibrous tissue connecting the parietal and temporal bones.
coronal suture 
Immobile joint made of fibrous tissue connecting the frontal bone and the two parietal bones.