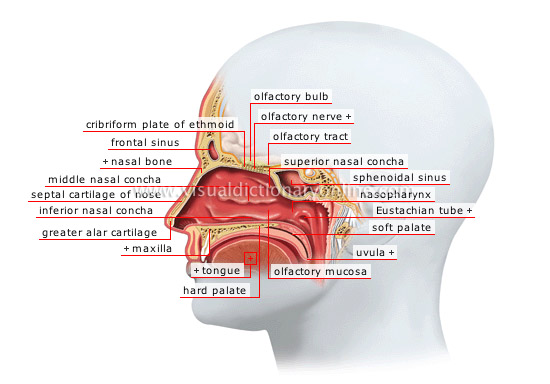
nasal fossae
Each of two cavities separated by a middle partition; they assist in olfaction, respiration and speech.
superior nasal concha 
Curved bony plate resting on the ethmoid and contributing to olfaction by bringing inhaled air into contact with the mucous membrane.
sphenoidal sinus 
Cavity hollowed out of the sphenoid bone of the skull; it connects with the nasal fossae and warms inhaled air.
uvula 
Fleshy movable appendage that is an extension of the posterior edge of the soft palate; it aids in ingesting food and speaking.
soft palate 
Muscular membranous section of the wall separating the mouth from the nasal cavity; it has a role especially in ingesting food and speaking.
Eustachian tube 
Tube connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx; it allows outside air to pass through, thus equalizing air pressure on both sides of the ear drum.
nasopharynx 
Section of the pharynx (meeting point of the respiratory and digestive tracts) through which the mouth connects with the nasal fossae and where the Eustachian tube opens.
hard palate 
Bony section of the wall dividing the mouth from the nasal cavity; it is extended by the soft palate.
maxilla 
Toothed bone forming the jaw. The upper jawbone forms a part of the palate. The lower jawbone is the only movable bone in the head.
greater alar cartilage 
Thin plate of resistant elastic tissue supporting the bridge of the nose and delimiting the contour of the nostril.
inferior nasal concha 
Curved bony plate attached to the lateral wall of the nasal fossae.
septal cartilage of nose 
Plate of resistant elastic tissue; it extends the bones of the nose and separates the nasal fossae.
middle nasal concha 
Curved bony plate resting on the ethmoid. Among its functions, the nasal chamber warms inhaled air by increasing the mucous surface.
nasal bone 
Small flat bone forming the skeleton of the root of the nose; the two nasal bones join along the bridge of the nose.
frontal sinus 
Cavity hollowed out of the frontal bone of the skull; it connects with the nasal fossae and warms inhaled air.
tongue 
Flexible muscular structure of the oral cavity; it helps in tasting, masticating and ingesting food, and also facilitates speech.
olfactory nerve 
Bundle of nerve fibers formed by the axons of the mucous membrane’s olfactory cells, which transmit nerve impulses to the brain.
olfactory mucosa 
Tissue lining a portion of the nasal fossae and containing olfactory cells, which detect odors and release nerve impulses.
olfactory tract 
Nerve structure containing the axons; it enables nerve impulses from the bulb to be carried to the brain, where they are interpreted.
olfactory bulb 
Nerve structure where fibers of the olfactory nerve end; it receives nervous impulses from the mucous membrane and transmits them to the olfactory tract.