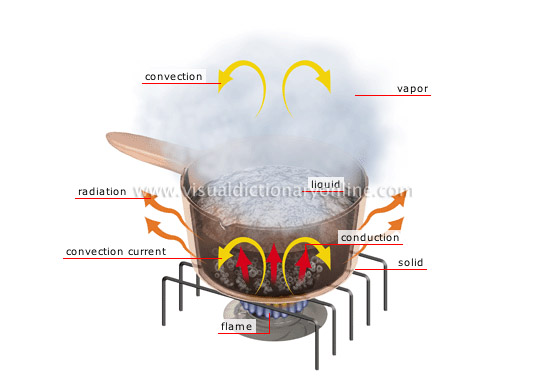
heat transfer
Heat transfer occurs in three ways that are related to molecular movement: conduction, convection and radiation.
liquid 
Matter having a definite mass and volume but no shape; its atoms are relatively mobile in relation to each other.
convection current 
Movement of fluid caused by a difference in density, which transfers heat. The heated water rises and is replaced by the cooler water from the surface.
flame 
Incandescent gas resulting from the combustion of a mixture of gas and air; it produces heat and light.
vapor 
Gaseous state of water above its boiling point (water boils and is converted to vapor at 212°F or 100°C).
solid 
Rigid body possessing mass, volume and a definite form; its atoms are linked to each other and are almost completely at rest.
radiation 
Heat generation in the form of electromagnetic waves emitted by a heated body (solid, liquid or gas).
convection 
Heat generation in a fluid that is caused by a variation in temperature resulting from the movement of molecules. Here, the heated water expands, rises and releases its heat to the surrounding air.
conduction 
Heat generation in a body (usually a solid) or between two bodies in contact; the molecules vibrate but no matter moves.