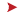
table of elements
Table created by Dmitry Mendeleyev in 1869 that classifies the now approximately 110 known chemical elements such as oxygen, hydrogen, iron and lead. The elements are classified in order of their atomic weight and arranged into groups having similar properties.
symbol 
The name of each chemical element is represented by one or two letters, the first of which is in uppercase (e.g., O for oxygen, Cl for chlorine).
atomic number 
Number that indicates the order of a chemical element in the table of elements and corresponds to the number of protons contained in its nucleus.
hydrogen 
This gas is the most abundant element in the universe and makes up part of the composition of water. It is used especially in petrochemistry and rocket engines.


 previous
previous