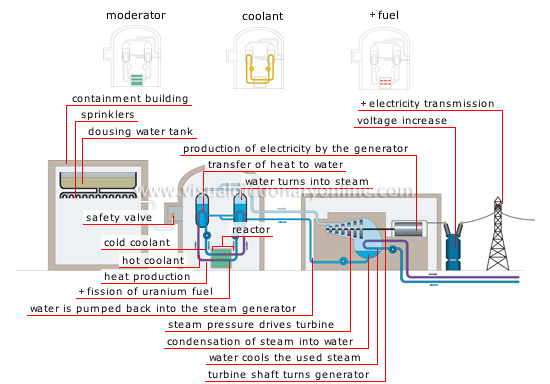
production of electricity from nuclear energy
A nuclear fission chain reaction is started and controlled inside the reactor to produce electricity.
cold coolant 
After releasing its heat to the steam generator, the cold coolant returns to the reactor.
transfer of heat to water 
The coolant releases the heat given off by the fission of uranium to the steam generator.
hot coolant 
The coolant extracts heat from the fuel and carries it toward the steam generator.
water turns into steam 
The hot coolant heats the water of the generator and brings it to the boiling point.
reactor 
Tightly sealed area where fission of the fuel is carried out in a controlled manner to release heat.
containment building 
Concrete building used to collect the radioactive steam from the reactor in the event of an accident.
dousing water tank 
Vat that contains water to cool the radioactive steam in the reactor in the event of an accident; this prevents a rise in pressure.
sprinklers 
Devices that release water to condense radioactive steam.
safety valve 
Device that lowers the pressure inside the reactor by discharging the radioactive steam to the containment building.
fission of uranium fuel 
The nuclei of the atoms break up; this frees neutrons and releases energy in the form of heat.
heat production 
The fission of atoms releases intense heat (between 575°F and 925°F), which is transmitted to the coolant.
production of electricity by the generator 
The generator produces electricity through the movement of the rotor in the stator.
turbine shaft turns generator 
The rotational movement of the turbine is transmitted to the generator’s rotor.
water is pumped back into the steam generator 
After passing through the turbine, water produced by the condensation of the steam returns to the steam generator.
water cools the used steam 
Cooling of the steam from the turbine is done with river or lake water.
condensation of steam into water 
At the turbine outlet, the steam cools and condenses into water.
electricity transmission 
Using high-voltage lines to transmit electricity over long distances reduces the strength of the current and, as a result, energy losses.
voltage increase 
At the outlet end of the power plant, the transformer increases the voltage; this reduces energy losses during transmission over long distances.
steam pressure drives turbine 
Steam from the steam generator turns the turbine runner, which is connected to the generator.
fuel 
Matter placed in the core of the reactor that contains heavy atoms (uranium, plutonium); energy is extracted from it by fission.
coolant 
Liquid or gas (including heavy water and carbon dioxide) that circulates inside the reactor; it harnesses and transports the heat released during fission of the fuel.
moderator 
Substance (ordinary water, heavy water, graphite) that slows the fast-moving neutrons emitted during fission to increase the probability of new collisions.