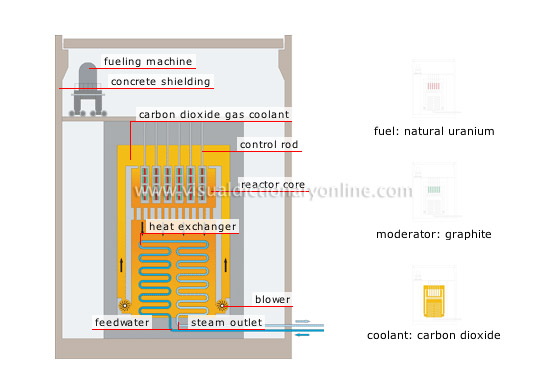
carbon dioxide reactor
Developed for the most part in Great Britain and France, it was replaced by the pressurized water reactor, which performs better and is less expensive.
carbon dioxide gas coolant 
Carbon dioxide that recovers the heat from the reactor core and transfers it to the heat exchanger.
feedwater 
Piping carries water from the condenser to the heat exchanger, where it is turned into steam.
steam outlet 
Water that has been vaporized in the carbon dioxide is carried to the turbine to produce electricity.
blower 
Device that circulates carbon dioxide in the reactor core.
heat exchanger 
Tubing system that is submerged in the hot carbon dioxide; here, water is turned into steam to power the turbine.
reactor core 
Center section of the nuclear reactor where fission reactions take place.
control rod 
Tube that contains a neutron-absorbing material (boron, cadmium) that is introduced into the reactor core to control its power.
concrete shielding 
Concrete structure that holds back radioactive products in the event of an accident.
fueling machine 
Remote-controlled device that inserts new fuel into the reactor.
fuel: natural uranium 
Natural uranium: fuel extracted from mines; it consists of a mixture of three uranium isotopes (uranium-234, -235 and -238).
coolant: carbon dioxide 
Carbon dioxide: gas that is heavier than air and is produced by burning graphite.
moderator: graphite 
Moderator: medium that slows the speed of the neutrons to maintain a continuous chain reaction.