thermal energy
Energy that is produced by turning water into steam through the burning of fuel (e.g., petroleum and coal) or through nuclear reaction.
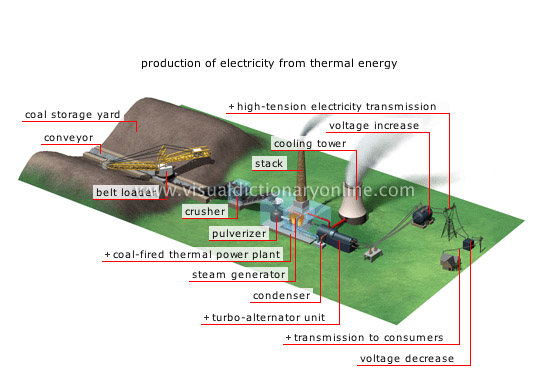
production of electricity from thermal energy 
The heat that is given off by burning combustible fuels in the thermal power plant converts water into steam; the steam turns a turbo-alternator unit to produce electricity.
condenser 
Circuit that cools the steam from the turbine and condenses it into water, which is reintroduced into the steam generator.
transmission to consumers 
Electricity is carried to areas of consumption over low-voltage distribution lines.
voltage decrease 
The transformer reduces the voltage in order to increase the strength of the current; this allows a greater number of consumers to be served.
high-tension electricity transmission 
Using high-voltage lines to transmit electricity over long distances reduces the strength of the current and, as a result, energy losses.
voltage increase 
At the outlet end of the power plant, the transformer increases the voltage; this reduces energy losses during transmission over long distances.
stack 
Pipe through which gases produced by burning coal are discharged; these gases are first partially cleaned to reduce pollution.
steam generator 
Device that uses the heat produced from burning coal to convert water into steam; the steam powers the turbo-alternator unit.
pulverizer 
Device that pulverizes coal into a very fine powder so that it burns more easily in the steam generator.
coal-fired thermal power plant 
Plant that produces electricity from thermal energy by burning coal.
crusher 
Device that pulverizes the coal carried by the conveyor belt into relatively fine fragments.
coal storage yard 
Area where the coal extracted from a mine is stored to ensure a continuous supply to the thermal power plant.
belt loader 
Movable materials-handling device that is fitted with an inclined conveyor belt; it is used mainly to raise loads.
conveyor 
Materials-handling device that consists of a conveyor belt (sturdy belt on rollers) that carries coal to the crusher.
turbo-alternator unit 
Device with a turbine that transmits the water’s mechanical energy to the alternator’s rotor to make it turn to produce electricity.
cooling tower 
Device that cools the heated water in the condenser through contact with the air; a small amount of water evaporates and the rest is reinjected into the condenser.