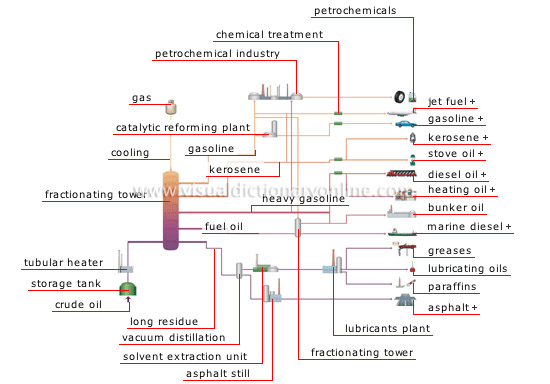
refinery products
Refining of crude oil yields hundreds of useful products.
paraffins 
Water-insoluble substances that have various uses; these include candle making, packaging and pharmaceutical products.
asphalt 
Mixture of bitumen and other substances that is used mainly to pave roads.
lubricating oils 
Viscous substances that are used mainly to reduce friction between two moving surfaces.
greases 
Pasty substances made of mineral oil and soap; they are used by industry to lubricate mechanical parts.
marine diesel 
Fuel especially designed for ships.
bunker oil 
Fuel used in high-powered heating systems and electric power plants; it is also used to power large diesel engines.
heating oil 
Fuel used in home heating systems and industrial installations requiring little energy.
diesel oil 
Fuel used mainly by the transportation industry to power diesel engines.
kerosene 
Fuel used for lighting and heating.
gasoline 
Motor fuel that is used mainly by the automotive industry to power internal combustion engines.
stove oil 
Fuel used mainly in home furnaces.
jet fuel 
Aviation fuel used to power jet engines.
petrochemicals 
Chemical products derived from petroleum-based products; they are found in fertilizers, detergents, plastics and other products.
chemical treatment 
Operation that improves the gasoline derived from crude oil by adding chemicals and mixing in kerosene to obtain jet fuel.
storage tank 
Large-capacity covered cylinder that is usually made of steel; crude oil is stored in it to maintain a constant rate of refining.
asphalt still 
Plant where bitumen (petroleum’s heaviest fraction) is treated and mixed with other substances to yield asphalt.
vacuum distillation 
Treatment that is used to separate out heavy residues at the bottom of the tower at low boiling temperatures.
lubricants plant 
Plant where base oils are treated (including the extraction of paraffin and the injection of additives) to obtain various lubricants.
crude oil 
Natural mineral oil that is made up of various hydrocarbons; it has been extracted from an oil deposit and not refined at all.
heavy gasoline 
By-product of the fractionation of crude oil that is chemically treated to provide motor fuels and specialized fuels.
kerosene 
By-product of the fractionation of crude oil that is chemically treated to provide various lighting and heating fuels.
fractionating tower 
Column used to separate fuel oil into its various fractions by vaporization and condensation to obtain various motor fuels.
fuel oil 
By-product of the fractionation of crude oil; after treatment, motor fuels and specialized heating fuels are derived from it.
long residue 
Residue made up of heavy nonvaporized fractions; it accumulates at the base of the fractionating tower after the hydrocarbons have been separated.
tubular heater 
Furnace with tubes that heats the crude oil to partially convert it to vapor before it enters the fractionating tower.
fractionating tower 
Column used to separate crude oil into its various fractions according to their boiling points; the light fractions rise to the top of the column.
gasoline 
Light fraction yielded by the first petroleum distillation; it is used mainly as motor fuel.
cooling 
Operation that cools the vapor at the top of the tower (condensation) in order to separate out hydrocarbons such as butane and propane.
petrochemical industry 
Plant that treats petroleum-based raw materials (crude oil and natural gas) to obtain marketable chemical products.
gas 
By-product (butane, propane) of the refining of crude oil; it is used as fuel in the home and as motor fuel.