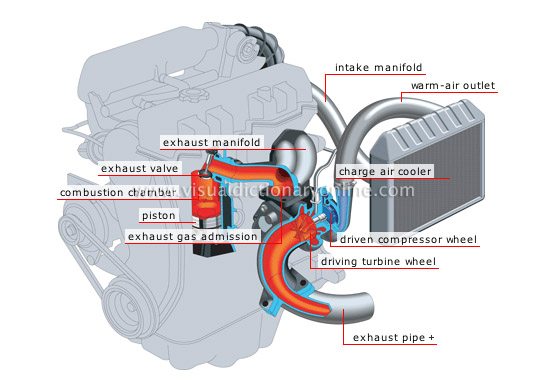
turbo-compressor engine
Engine equipped with a device combining a turbine with a compressor, which increases the amount of air entering the engine to increase its efficiency.
exhaust pipe 
Tubular conduit conducting the exhaust gases from the turbo-compressor to the muffler.
combustion chamber 
Part of the cylinder in which the pressurized air/fuel mixture is ignited and burned.
piston 
Metal moving part in the cylinder and attached to the connecting rod; it compresses the air/fuel mixture, then receives the thrust from the burned gases.
exhaust valve 
Part that opens to allow the burned gases to escape.
driving turbine wheel 
Part converting the energy from the exhaust gases into rotational energy to activate the compressor.
driven compressor wheel 
Part integrated with the driving turbine wheel; it spins very quickly as it draws in air and compresses it.
charge air cooler 
The heat exchanger cools the compressed air before it enters the cylinders.
exhaust manifold 
Set of pipes at the exit of the cylinders; it captures the exhaust gases and conducts them to the turbo-compressor.
warm-air outlet 
When compressed, the temperature of the air increases greatly, which can make it less effective.
intake manifold 
After cooling, the air is again conducted to the combustion chamber, which takes in more air.
exhaust gas admission 
The flow of the exhaust gas is conducted directly from the combustion chamber to the turbo compressor to drive the turbine.