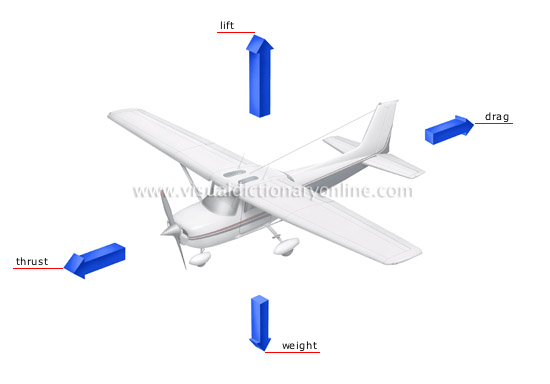
forces acting on an airplane
Physical phenomena that affect the movement of an aircraft in flight.
weight 
Force resulting from the effect of the Earth’s gravity acting on the aircraft’s mass; the force of the engines must overpower this to keep the aircraft in the air.
drag 
Force opposite to thrust that creates resistance to the aircraft’s forward movement and must be reduced.
lift 
Force exerted on an aircraft’s wings to keep it in the air when a certain forward speed is reached.
thrust 
Force developed by the engine’s propeller pulling it forward; in jet aircraft, thrust is created by the force of the ducts.