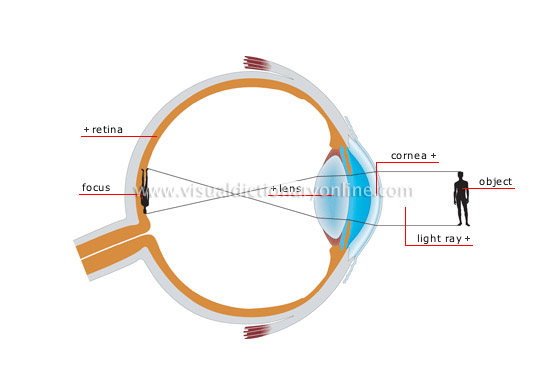
normal vision
The image of an object is formed on the retina after passing through the lens, which, depending on the distance of the object, expands or contracts to give a sharp image.
retina 
Inner membrane at the back of the eye covered in light-sensitive nerve cells (photoreceptors); these transform light into an electrical impulse that is carried to the optic nerve.
lens 
Transparent elastic area of the eye; focuses images on the retina to obtain clear vision.
light ray 
Line along which light emanating from an object propagates. The retina converts light rays into nerve impulses, which are then interpreted by the brain.
cornea 
Transparent fibrous membrane extending the sclera and whose curved shape makes light rays converge toward the inside of the eye.
focus 
Point where light rays converge to form an image; the brain interprets the retina’s upside-down image as right-side-up.
object 
Light rays emanating from an object pass through the eye’s various media to form an inverted image on the retina.