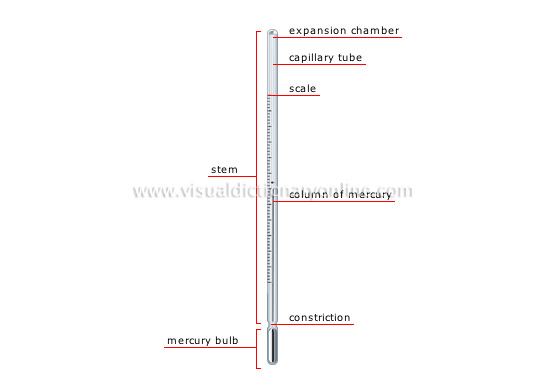
clinical thermometer
More precise than the alcohol thermometer, it is used to take the temperature of the human body; it is graduated from 94°F to 108°F.
expansion chamber 
Space that is taken up by the gas in the capillary bore; it is pushed back as the mercury rises into it.
stem 
Glass tube containing the capillary bore.
capillary tube 
End of the glass tube in which the mercury rises or falls with the temperature; the mercury thermometer tube is filled with gas.
scale 
Divisions of equal length (degrees) marked on the thermometer that constitute the units of measurement.
column of mercury 
Quantity of mercury that is contained in the capillary bore; its height varies with the temperature.
constriction 
Narrowing that prevents the mercury from spontaneously dropping into the bulb as the temperature lowers (the thermometer must be shaken to make it go down).
mercury bulb 
Glass reservoir containing mercury (a liquid metal) that expands and rises in the capillary tube as the temperature rises.