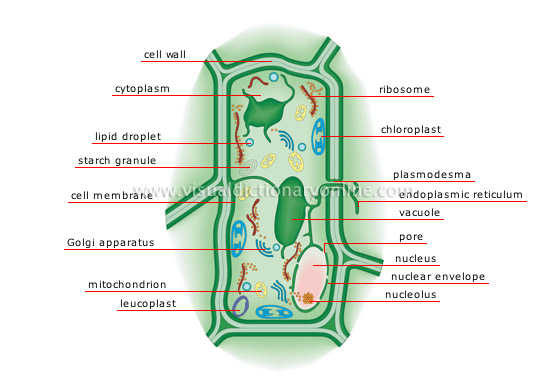
plant cell
Smallest living structure and the constituent element of all vegetables; it varies in size and shape depending on its function.
leucoplast 
Small colorless structure that produces and stores starch, the vegetable’s food.
mitochondrion 
Ovoid organelle that produces the energy necessary for cell activity.
Golgi apparatus 
Organelle composed of a series of pockets that receive proteins produced by the ribosomes and either transport them outside the cell or to other organelles.
vacuole 
Spherical cavity containing water, waste and various substances required by the cell.
cell membrane 
Casing that covers the cell’s cytoplasm; it acts as a filter, controlling the passage of certain substances in and out of the cell.
starch granule 
Concentric layers of starch produced by the cell and stored for food.
lipid droplet 
Small sac filled with essential fatty acids that are produced by the cell and stored for food.
cytoplasm 
Clear gelatinous substance surrounding the various cellular structures.
nucleolus 
Small spherical body located inside the nucleus, within which the ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures, are produced.
nuclear envelope 
A double-layered membrane enveloping the nucleus.
nucleus 
Organelle containing a cell’s genes and controlling its activities.
pore 
Perforations in the nuclear envelope allowing for exchanges between the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
endoplasmic reticulum 
Interconnecting tubes allowing substances to be transported within the cell or between the cell and its exterior environment.
plasmodesma 
Perforations in the membranes allowing two adjacent cells to exchange cytoplasm.
chloroplast 
Small structure, containing a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs solar energy and uses it to produce glucose, the vegetable’s food.
ribosome 
Small structure, occasionally attached to the endoplasmic reticulum; it generates proteins essential to the formation and functioning of living things.
cell wall 
Stiff exterior surface of the cytoplasmic membrane that gives the cell its shape.