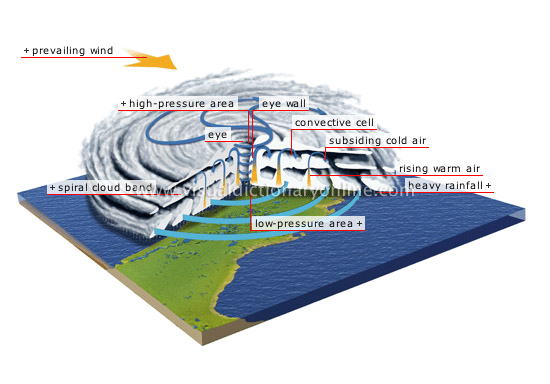
tropical cyclone
Low-pressure zone that forms in the intertropical region and is marked by violent precipitation and swirling winds of 74 to 185 mph.
low-pressure area 
A rising column of air causes a decrease in air pressure on the ocean’s surface.
spiral cloud band 
eye 
Relatively calm zone in the center of the cyclone, with light winds and very few clouds; it is about 20 mi in diameter.
rising warm air 
A hot air column forms when the ocean’s surface is warmed by the Sun.
heavy rainfall 
subsiding cold air 
Cool air that reaches the top of the clouds and once again descends, becoming warmer as it becomes more compressed.
convective cell 
Phenomenon formed by hot humid air that rises and condenses to form a cloud, and a descending current of cold air.
eye wall 
Thick layer of cloud that swirls around the eye; it has the most powerful winds (up to 185 mph) and the most intense precipitation.
high-pressure area 
Column of ascending air that causes a rise in upper air pressure, at the top of the most developed clouds.
prevailing wind 
It moves the cyclone forward at an average speed of 15 mph.