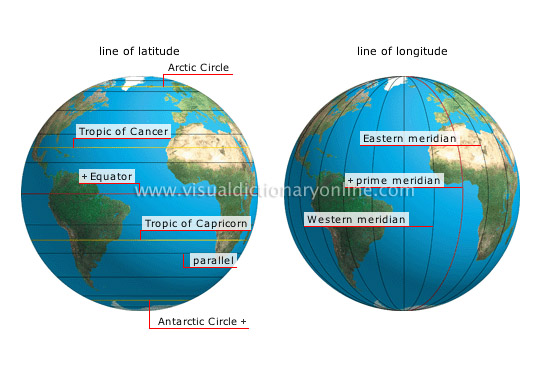
grid system
Collective term for the parallels and meridians that form an imaginary grid over the Earth’s surface, making it possible to locate a specific point.
line of longitude 
Coordinate of a point on the Earth’s surface indicating, in degrees, its distance from the prime meridian.
Western meridian 
Imaginary line connecting the poles and perpendicular to the Equator; located west of the Greenwich meridian.
prime meridian 
Chosen by convention as the meridian of origin; its longitude, 0, divides the Eastern and Western hemispheres.
Eastern meridian 
Imaginary line connecting the poles and perpendicular to the Equator; located east of the Greenwich meridian.
line of latitude 
Coordinate of a point on the Earth’s surface indicating, in degrees, its distance from the Equator.
Arctic Circle 
Parallel of latitude 66°34' N; it marks the polar zone, where days and nights last 24 hours during solstices.
Equator 
Imaginary line encircling the Earth at its greatest circumference and perpendicular to the polar axis; its latitude, 0, serves as a reference point for calculating other latitudes.
Tropic of Capricorn 
Parallel located at 23°26' N latitude (a distance of about 1,600 mi from the Equator).
parallel 
Imaginary circle whose plane is parallel to the Equator.
Tropic of Cancer 
Parallel located at 23°26' N latitude (a distance of about 1,600 mi from the Equator).
Antarctic Circle 
Parallel of latitude at 66°34' S; it marks the polar zone, where days and nights last 24 hours during solstices.