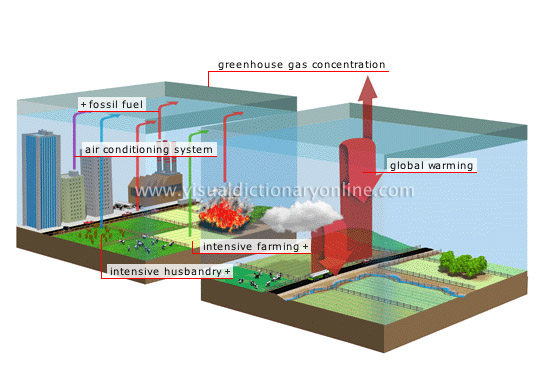
enhanced greenhouse effect
Human activity constantly emits greenhouse gases, which trap ever more heat in the atmosphere.
air conditioning system 
Air conditioning systems use chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) that absorb infrared rays and damage the ozone layer.
intensive husbandry 
Raised in great numbers, ruminants emit methane as a by-product of digestion.
intensive farming 
To obtain the maximum yield, intensive farming uses chemical fertilizers that are responsible for various forms of air and water pollution.
global warming 
Temperatures have increased by 0.5% in the last century; continued rises in temperature could result in major climate changes.
greenhouse gas concentration 
Increasingly abundant greenhouse gases reflect more and more infrared rays toward the Earth’s surface, accelerating global warming.
fossil fuel 
The combustion of wood and fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) emits carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere.