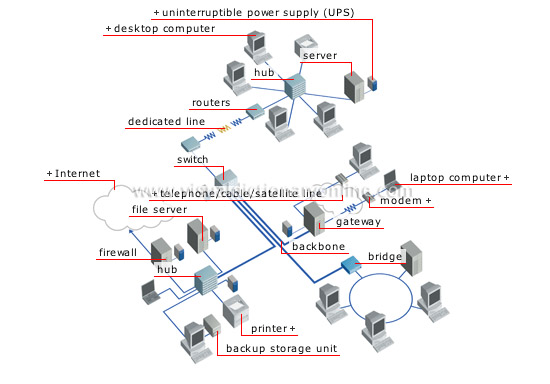
wide area network
Private or public network spanning a large area (a region or country); it usually brings together several local area networks.
hub 
Unit that receives all messages sent by the devices connected to it and redistributes them to all users.
uninterruptible power supply (UPS) 
Device used to regulate the power supply to the computer and its peripherals by limiting the effects of cuts, surges or dips in the electric circuit voltage.
laptop computer 
Small stand-alone microcomputer with a screen and integrated keyboard; it is powered by an internal battery.
modem 
Device that converts digital signals into analog signals so that computers can communicate with each other over telephone lines.
telephone/cable/satellite line 
Linking of off-site devices by telephone network, cable network or telecommunications satellite.
bridge 
Interconnecting device linking similar networks.
backup storage unit 
Storage peripheral used to copy data onto a removable medium to facilitate retrieval in the event of loss.
printer 
Output peripheral allowing computer-generated characters, images and graphics to be reproduced on paper.
Internet 
Global network consisting of thousands of public and private networks of varying sizes; it is linked by a set of standard communications protocols.
firewall 
Device controlling data that circulate between a public network (such as the Internet) and a private network; it prevents unauthorized access to the latter.
file server 
Server hosting a set of data files that are at the disposal of all computers connected to the network.
gateway 
Interconnecting device linking different networks.
switch 
Unit establishing the connections needed to route data to intended users from one branch of a network to another; it also handles traffic between the various parts of a network.
backbone 
Main artery of a network characterized by a high throughput; it transmits data between secondary networks.
dedicated line 
Telephone or cable communications link reserved for one use or for a specific user.
desktop computer 
Small workstation or microcomputer designed for stationary use.
routers 
Interconnecting devices ensuring transmission of data between two or more networks by determining the best path for them.
server 
Computer that hosts various resources (including files, applications and databases) and places them at the disposal of all the devices connected to the network.
hub 
Unit that receives all messages sent by the devices connected to it and redistributes them to all users.