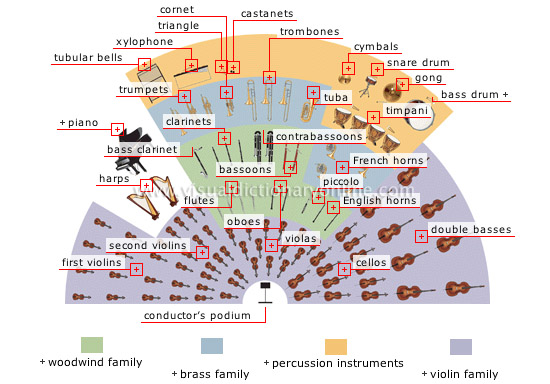
symphony orchestra
Group composed of numerous musicians under the direction of a conductor; it includes various categories of instruments, depending on the work to be performed.
bassoons 
Double-reed instruments consisting of a curved conical wooden tube; the double-reed is inserted into a curved mouthpiece.
tuba 
Valved instrument whose tonal range is the lowest in the brass family; it consists of a coiled conical tube and an upturned bell.
cymbals 
Instrument consisting of two metal disks that are struck together.
snare drum 
Flat drum consisting of two membranes; stretched across the lower head are snares that produce a rattling sound.
gong 
Instrument consisting of a large metal disk with a raised central portion that is struck using a mallet.
timpani 
Instruments consisting of a parabolic copper basin covered with a stretched batter head that is struck with a mallet.
bass drum 
Large drum set on a vertical frame and struck using a pedal-controlled wooden mallet.
French horns 
Valved instruments consisting of a coiled conical tube and a flared bell.
oboes 
Double-reed instruments consisting of a conical tube with holes (some closed by keys) and a slightly flared bell.
piccolo 
Small transverse flute whose range is an octave higher than the regular transverse flute.
double basses 
Four- or five-stringed instruments played upright; the largest of the violin family, they also have the lowest range.
English horns 
Alto oboes with a pear-shaped bell.
cellos 
Four-stringed instruments placed between the legs when played; they are about twice the size of a violin and their range is one octave lower than the viola.
conductor’s podium 
Small dais that the conductor stands on to direct the musicians as they play.
violas 
Four-stringed instruments similar to a violin but played a fifth lower.
second violins 
The violins that support the first violins.
first violins 
The violins that play the melody.
harps 
Plucked stringed instruments consisting of strings of unequal length attached to a triangular frame.
flutes 
Instruments with a side mouthpiece and a tube containing holes, some of which are closed by keys.
clarinets 
Single-reed instruments whose cylindrical tube contains holes (some closed by keys) and ends in a flared bell.
piano 
Piano whose mechanism is horizontal, allowing the pianist to better control the sound; it varies in size from 8 to 9 ft.
bass clarinet 
Clarinet with a curved tube; its range is one octave lower than the ordinary clarinet.
trumpets 
Valved instruments consisting of a curved cylindrical tube and a flared bell.
tubular bells 
Series of metal tubes arranged vertically in order of size; small hammers are used to strike the tops of the tubes.
contrabassoons 
Double-reed wind instruments consisting of several tubes; their range is one octave lower than the bassoon.
cornet 
Valved instrument consisting of a curved conical tube and a flared bell.
xylophone 
Instrument consisting of wooden bars placed on top of resonators arranged in chromatic order in two rows; the bars are struck with mallets.
triangle 
Instrument composed of a metal bar bent to form a triangle open at one end; the triangle is struck with a metal rod.
trombones 
Instruments consisting of a curved tube with a slide that is lengthened to produce notes varying in pitch by semitones.
castanets 
Instrument composed of two shell-shaped pieces of wood held in one hand and struck together using the fingers.
violin family 
Group of stringed instruments played with a bow.
percussion instruments 
Group of instruments that are struck directly with the hands or with sticks, mallets, etc. to produce a sound.
brass family 
Group of wind instruments made from metal and played with cup-shaped mouthpieces.
woodwind family 
Group of wind instruments originally made from wood.