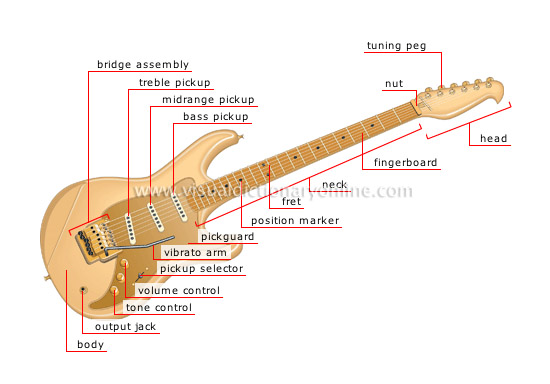
electric guitar
Guitar with microphones that convert string vibrations into electric signals, which are then amplified and converted into sound.
bridge assembly 
Assembly consisting of the bridge, the tailpiece and the vibrato arm.
head 
The upper end of the neck where the tuning pegs are attached.
neck 
Part of the guitar separated into sections by frets and along which the strings are stretched.
fret 
Metal piece that acts as a reference point along the string, dividing the neck into sections separated by a semitone.
position marker 
Piece of mother-of-pearl, wood or plastic imbedded into the center of certain sections of the neck.
fingerboard 
Board on which the player’s fingers are placed to control the length of the vibrating string to determine the pitch of a note.
nut 
Small piece glued to the top of the neck; its function is to separate the strings and raise them between the head and the bridge.
tuning peg 
Device that adjusts the tension of the strings.
pickguard 
Piece that covers the electric components inside the body, usually made of plastic.
vibrato arm 
Device that raises and lowers the bridge to adjust string tension and thereby alter the pitch of the notes.
pickup selector 
Button that allows the player to choose one microphone or combine several.
volume control 
Button that controls the loudness of the instrument.
tone control 
Button that adjusts the frequency of the electric signals in order to control the tone of the guitar.
output jack 
Plug for the cable that transmits the electric signals to the amplifier.
body 
Hollow nonresonant part of the instrument where the guitar’s electrical components are housed.
treble pickup 
Device that converts high-frequency string vibrations into electric signals.
midrange pickup 
Device that converts middle-frequency string vibrations into electric signals.
bass pickup 
Device that converts low-frequency string vibrations into electric signals.