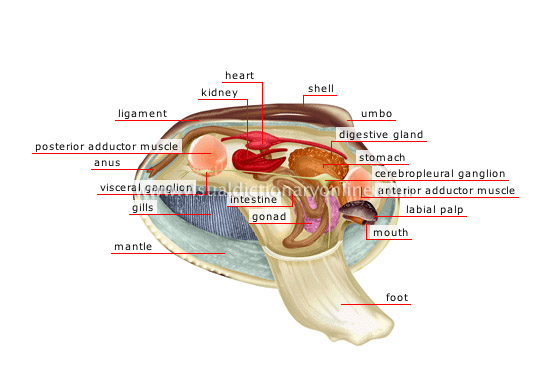
anatomy of a bivalve shell
shell 
Calcareous casing produced by the mantle; it has three layers and protects the main organs of the mollusk.
ligament 
Corneous structure located behind the umbones and joining both valves of the shell; its elasticity allows them to pull apart.
umbo 
Protuberance at the terminal end of the valve, from which the shell grows.
mantle 
Thick fold of tissue forming two lateral lobes; it envelops the organic mass of the mollusk and secretes its shell.
intestine 
Section of the digestive tract between the stomach and the anus where absorption of nutrients is carried out and waste is transformed into fecal matter.
cerebropleural ganglion 
Small sac located near the anterior abductor muscle; the nervous system is made up of three pairs of ganglia (cerebropleural, visceral and pedal).
visceral ganglion 
Small sac located near the posterior abductor muscle; the nervous system is made up of three pairs of ganglia (cerebropleural, visceral and pedal).
anus 
Terminal orifice of the digestive tract enabling ejection of fecal matter.
posterior adductor muscle 
Powerful muscle attached to both inside surfaces of the valves; it contracts to open or close them quickly.
kidney 
Organ secreting urine; it eliminates toxic substances from the body.
heart 
Muscular organ helping blood to circulate.
digestive gland 
Organ producing a secretion that contributes to digestion.
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract preceding the intestine; it receives food to be digested.
anterior adductor muscle 
Muscle attached to both inside surfaces of the valves that contracts to open or close them quickly; it is less powerful than the posterior abductor muscle.
labial palp 
Mouthpart that grasps food particles deposited on the gills and carries them to the mouth.
mouth 
Anterior cavity of the digestive tract surrounded by four labial palps, which enable food particles to enter.
gonad 
Genital gland producing spermatozoa (sperm) or ova (eggs), depending on the sex of the mollusk.
gills 
Respiratory organs located between the foot and the mantle, formed of two layers of ciliated filaments, which filter water and retain food particles.