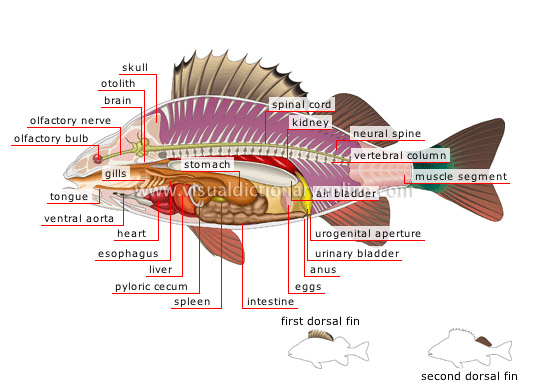
anatomy of a perch
Perch: snub-nosed bony freshwater fish with an oval body and a spiny dorsal fin; the flesh of this fish is highly valued.
muscle segment 
Muscular segment of the posterior portion of the body; its zigzag arrangement contributes to efficient motion.
skull 
Bony structure enclosing and protecting the brain.
urogenital aperture 
Opening common to the genital and urinary tracts allowing the evacuation of gametes and urine.
air bladder 
Flexible air-filled sac located above the viscera; it allows the fish to remain buoyant at a specific depth.
vertebral column 
Movable bony axis made up of various parts articulating with each other (vertebrae); it supports the skeleton and contains the spinal cord.
spinal cord 
Component of the nervous system made up of a soft fatty substance and forming a cylindrical stem inside the vertebral column.
neural spine 
Bony stem of the nervous system connected to the vertebral column and forming the skeleton.
kidney 
Organ that eliminates metabolic waste and maintains the pressure of internal fluids.
intestine 
Section of the digestive tract between the stomach and the anus where absorption of nutrients is carried out and waste is transformed into fecal matter.
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract preceding the intestine; it receives food to be digested.
pyloric cecum 
Lateral canal of the digestive tract where a part of digestion mainly occurs, as well as fermentation.
esophagus 
Canal of the anterior portion of the digestive tract; it carries food to the stomach.
heart 
Muscular organ helping blood to circulate.
ventral aorta 
Canal circulating the blood from the heart to the gills, then on through the head and the rest of the body.
gills 
Respiratory and excretory organs (four pairs) each formed of two layers of filaments; they enable water to exchange oxygen and ammonium as it circulates over the gills.
tongue 
Elongated movable mouthpart having a gustatory function; it allows the fish to swallow its food.
olfactory bulb 
Enlargement of the anterior terminal end of the olfactory nerve where its roots come together.
olfactory nerve 
Cranial cord connecting the brain to the olfactory bulb.
brain 
Main organ of the nervous system that is made up of nerve centers; it is located in the upper portion of the head and is protected by the skull.
otolith 
Small calcareous structure of the inner ear ensuring the fish’s equilibrium in the water.
urinary bladder 
Reservoir in which urine from the kidneys collects before being evacuated through the urogenital aperture.
liver 
Viscera that secretes bile, among other substances; bile helps digestion.
spleen 
Organ of the circulatory system where impurities in the blood are destroyed.
anus 
Terminal orifice of the digestive tract enabling ejection of fecal matter.
eggs 
In fish, the female produces eggs in the ovaries and the male produces soft roe in the testicles; the eggs and roe are expelled into the water, where fertilization occurs.
first dorsal fin 
Swimming appendage formed of a membrane and usually prickly rays located on the middle anterior dorsal portion of the body; it provides stability.
second dorsal fin 
Swimming appendage formed of a membrane and rays located on the middle posterior dorsal portion of the body; it provides stability.