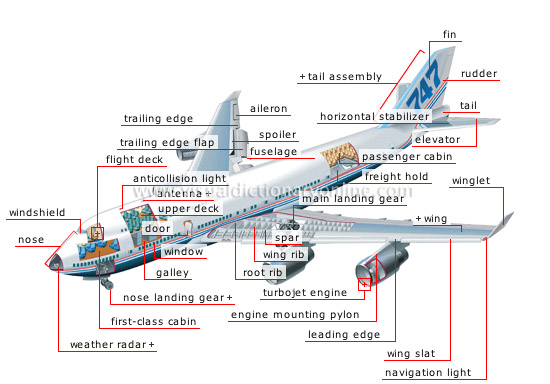
long-range jet
Aircraft that transports passengers and cargo traveling long distances at high altitudes (between 30,000 and 40,000 ft).
first-class cabin 
Most comfortable part of the cabin where passengers receive special attention; it is always situated at the front of the aircraft.
weather radar 
Device that is used by the technical crew to evaluate weather conditions.
nose landing gear 
Retractable mechanism that enables the aircraft to land; it is located at the front end.
galley 
Compartment where meals for service are prepared.
window 
Airtight window that lets natural light into the cabin.
spar 
Metal girder placed in the direction of the wingspan to absorb bending stress.
wing rib 
Metal part of the wing’s frame that is perpendicular to the spars.
root rib 
Metal part that connects the wing to the fuselage.
door 
Airtight door for entering the cabin; some doors are used only in emergencies.
windshield 
Highly durable pane made of glass and plastic that provides good visibility.
nose 
Leading tip of the fuselage.
flight deck 
Compartment that contains all the navigation and control equipment; the navigation crew pilot the aircraft from here.
anticollision light 
Bright red light that is visible from all directions to signal the aircraft’s presence.
upper deck 
Upper floor on very large aircraft that contains the flight deck and a passenger cabin.
antenna 
Antenna that receives and transmits radio signals to communicate with the control tower or another aircraft.
trailing edge flap 
Articulated flap on the trailing edge of the wing that deploys downward to increase the aircraft’s lift on takeoff.
spoiler 
Articulated flap on top of the wing that is deployed immediately after landing; it increases drag and reduces lift to slow the aircraft.
trailing edge 
Back edge of the wing.
aileron 
Hinged flap on the trailing edge of the wing near the tip for controlling the aircraft’s roll.
passenger cabin 
Compartment in which most of the passengers travel and receive basic services; it is also called economy class.
wing 
Horizontal surface on which aerodynamic forces are exerted to keep the aircraft in the air.
turbojet engine 
Jet-propulsion turbine producing hot gases that are expelled at high speed to provide the thrust necessary to propel the aircraft.
engine mounting pylon 
Structure that attaches a turbojet engine to a wing.
wing slat 
Articulated flap on the wing’s leading edge; it is deployed on takeoff and landing to increase lift.
leading edge 
Front edge of the wing.
navigation light 
Light signaling the direction in which the aircraft is flying: red on the left wing (port), green on the right wing (starboard) and white on the tail.
winglet 
Protruding surface at the wingtip that enhances aerodynamics.
main landing gear 
Retractable mechanism that enables the aircraft to land; it is located behind the aircraft’s center of gravity under its wings.
freight hold 
Compartment where baggage and cargo are stored.
horizontal stabilizer 
Wing made up of the fixed horizontal tail assembly; it stabilizes the aircraft horizontally.
elevator 
Articulated flap that is attached to the trailing edge of the horizontal stabilizer; it is used to change altitude and correct any pitch that may occur.
fuselage 
Aircraft body that is divided into several compartments and whose aerodynamic form reduces air friction; it is supported by the wings in flight.
tail assembly 
Moving and fixed surfaces that are located at the tail of the aircraft for steering and stabilizing it.
tail 
Rear part of the fuselage.
rudder 
Articulated flap at the rear of the fin that steers the aircraft and corrects any yaw that might occur.
fin 
Fixed vertical part of the tail assembly that keeps the aircraft stable.