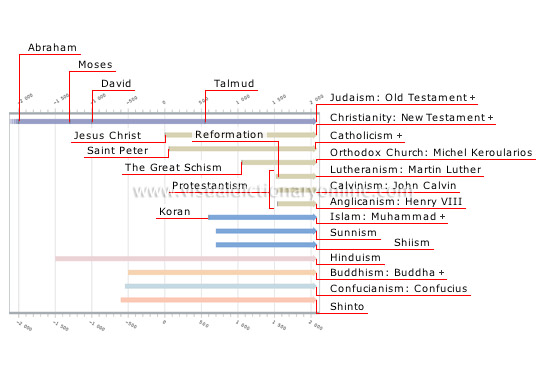
chronology of religions
Religions have usually been signalized by a prophet or an event; they have overlapped and influenced one another throughout the course of history.
Jesus Christ 
Prophet regarded by Christians as the Son of God; he was crucified and resurrected three days later.
David 
King of Israel and considered to be the founder of Jerusalem; many of the psalms in the Old Testament are attributed to David.
Calvinism: John Calvin 
Protestant religion based on the theology of John Calvin, who founded Protestantism in France.
Talmud 
Compilation of writings on Jewish law by generations of scholars and rabbis.
Koran 
Sacred text of Muslims; it contains the revelations made by Allah to the prophet Muhammad.
The Great Schism 
Split between the Church of Rome and the Eastern Orthodox Church in Constantinople; it came about because the Greeks refused to recognize the authority of the pope in Rome.
Saint Peter 
Apostle of Jesus Christ who is considered to have been the first pope of Rome.
Moses 
God dictated the Ten Commandments to Moses on Mount Sinai.
Abraham 
The first biblical patriarch who is regarded as the ancestor of the Jewish people; God made his covenant with Abraham.
Shinto 
Polytheistic religion of Japan with divinities such as stars, animals and plants that personify natural forces; Shintoists venerate the emperor.
Confucianism: Confucius 
Religion of China named after the philosopher Confucius, whose teachings emphasize the natural order and hierarchy of things and the importance of being in harmony with nature.
Buddhism: Buddha 
Asian religion named after a sage from India who taught that the aim of life is to abolish suffering and to achieve enlightenment or nirvana.
Hinduism 
Polytheistic religion of India made up of a complex body of ideas, beliefs and practices.
Shiism 
Branch of Islam that resulted from the schism initiated by Muslims who contested the succession of Abu Bakr; they regarded Ali, son-in-law of Muhammad, as the rightful caliph.
Sunnism 
Branch of Islam that observes the Sunna, a body of traditional Muslim law based on the teachings and acts of Muhammad.
Islam: Muhammad 
Religion of Muslims, who believe in Allah as the sole deity; Islam was founded by the prophet Muhammad and its teachings are collected in the Koran.
Lutheranism: Martin Luther 
Protestant religion founded by Martin Luther, a German theologian; in 1517, he wrote 95 theses condemning certain papal practices.
Anglicanism: Henry VIII 
Protestant religion of the Church of England; when the pope refused to grant him a divorce, Henry VIII provoked a schism with Rome.
Protestantism 
The Christian churches that grew out of the Reformation; Protestantism posits a personal relationship with Christ requiring no intermediary.
Orthodox Church: Michel Keroularios 
The Eastern Christian churches that separated from Rome in 1054; Michel Keroularios, the patriarch of Constantinople, initiated the Great Schism.
Catholicism 
Christian religion that recognizes the authority of the pope in matters of dogma and morality.
Judaism: Old Testament 
Religion that holds that the Jews are God’s chosen people; the Old Testament tells the story of the covenant between God and the people of Israel.
Christianity: New Testament 
Religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ as related in the New Testament, which is made up mainly of the Gospels and Epistles.