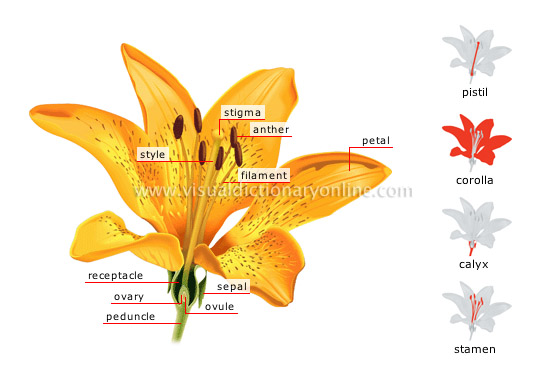
structure of a flower
peduncle 
Terminal offshoot of the stem or twig; it first connects the flower, then the fruit, to the plant.
ovule 
Small rounded structure produced by the ovary and containing the female cell; after fertilization, the seed develops from it.
ovary 
Hollow structure containing one or more ovules; the fruit usually develops from it after fertilization.
receptacle 
Enlarged portion of the peduncle containing and supporting the other parts of the flower.
sepal 
Usually green part of the flower that protects the flower’s internal structures; it may fall after flowering occurs or remain until the fruit has ripened.
petal 
Usually colorful and scented part of the flower that surrounds the male and female reproductive organs; it often helps attract pollinators.
anther 
Upper part of the male floral organ (stamen) that produces pollen grains; at maturity, it splits to release them.
filament 
Cylindrical axis connecting the anther to the rest of the flower.
stigma 
Upper part of the female floral organ (pistil) that receives and holds pollen.
style 
Cylindrical axis connecting the stigma to the ovary.
pistil 
Each of the female floral organs at the flower’s center, consisting of an ovary, a stylus and a stigma.
calyx 
Part of the flower composed of all its sepals.
stamen 
Each of the male floral organs, consisting of a filament and an anther.
corolla 
Part of the flower composed of all its petals.