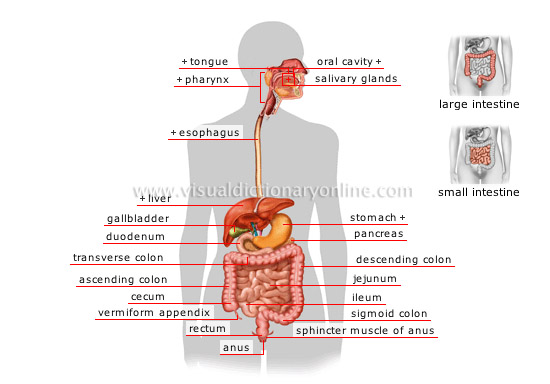
digestive system
Formed of the mouth, digestive tract and appended glands, it converts ingested food so that it can be assimilated by the organism.
ileum 
Terminal part of the small intestine between the jejunum and cecum.
jejunum 
Middle section of the small intestine between the duodenum and the ileum; the majority of nutrients are absorbed here.
duodenum 
Anterior section of the small intestine; secretions from the liver and pancreas, as well as food partially digested in the stomach, empty into it.
pancreas 
Digestive gland connected to the duodenum; produces secretions and hormones (especially insulin).
stomach 
Dilated section of the digestive tract; it stores, stirs and mixes food with the gastric juices it secretes before emptying it into the duodenum.
esophagus 
Muscular membranous channel of the anterior section of the digestive tract; it allows food to reach the stomach.
pharynx 
Muscular membranous channel connecting the nasal cavity to the larynx and the oral cavity to the esophagus; it enables breathing, ingestion of food and speech.
rectum 
Terminal section of the large intestine preceding the anus.
sphincter muscle of anus 
Muscle ensuring the contraction and relaxation of the anus and enabling defecation.
anus 
Terminal orifice of the digestive tube controlled by a sphincter enabling ejection of fecal matter.
sigmoid colon 
Fourth segment of the colon; it carries waste to the rectum.
cecum 
Anterior part of the large intestine; it receives food particles from the ileum.
ascending colon 
First segment of the colon; it absorbs water from food residue before it is excreted.
descending colon 
Third segment of the colon; it stores waste before it is eliminated.
transverse colon 
Second segment of the colon (middle section of the large intestine). The right colon (the ascending colon plus half the transverse colon) mainly enables absorption of water.
gallbladder 
Small reservoir where bile secreted by the liver gathers before emptying into the duodenum during digestion. Bile helps in the digestion of fatty substances.
liver 
Viscera secreting substances, including bile, that help digestion and break up certain toxins contained in the blood.
salivary glands 
Each of the three pairs of organs secreting a liquid (saliva) that contains a digestive enzyme; it is used to moisten food to facilitate its ingestion.
tongue 
Flexible muscular structure of the oral cavity; it helps in tasting, masticating and ingesting food, and also facilitates speech.
oral cavity 
Anterior cavity of the digestive tract enabling ingestion of food; it also aids in breathing.
small intestine 
Narrow section of the digestive tract, about 20 ft long, between the stomach and cecum, where a part of digestion and food absorption occurs.
large intestine 
Last wide section of the digestive tract, about 5 ft long, where the final stage of digestion and elimination of waste occurs; it includes the colon and the rectum.
El Diccionario Visual, a new valuable resource to learn Spanish. Includes 17 all-around themes to explore, including the human body, sciences and food.