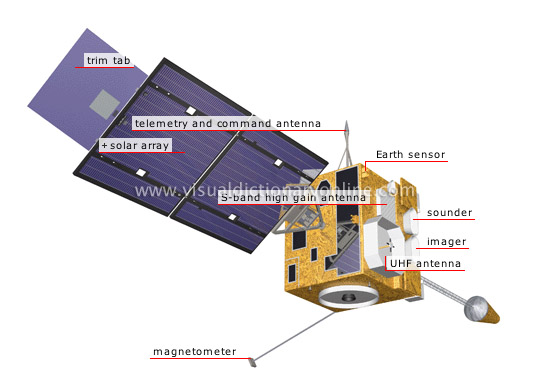
geostationary satellite
A satellite that travels in a geostationary orbit, allowing it to observe a considerable area of the Earth’s surface on a continuous basis.
trim tab 
Adjustable mechanical component that makes it possible to modify the satellite’s position.
solar array 
Power supply device that converts solar energy into immediately usable electrical energy.
magnetometer 
Instrument designed to measure the Earth’s magnetic field.
UHF antenna 
Antenna that provides a radio link with terrestrial stations.
imager 
Radiometer that generates images of clouds and of the surface of the Earth and the oceans.
sounder 
Radiometer designed to measure temperature and humidity at different altitudes in the atmosphere.
telemetry and command antenna 
It allows terrestrial stations to monitor satellite operations and transmit commands to the satellite.
S-band high gain antenna 
Main antenna pointed toward the Earth to transmit large quantities of scientific data.
Earth sensor 
Instrument that locates the Earth’s horizon so that the antenna can be positioned correctly.