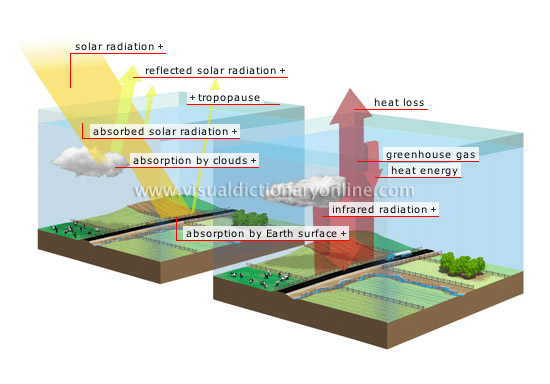
natural greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is an indispensable natural phenomenon; without it, the average temperature, currently 59°F, would be no higher than 0°F.
reflected solar radiation 
Thirty percent of solar radiation is sent back into space by clouds, by particles suspended in the atmosphere and by the Earth’s surface.
tropopause 
Boundary between the troposphere, where meteorological phenomena are produced, and the stratosphere, which absorbs a large part of solar radiation.
heat loss 
Part of the infrared rays reflected by the Earth’s surface is not absorbed and dissipates in space.
greenhouse gas 
Gas that traps heat in the atmosphere; composed mainly (60%) of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (15%) and CFCs (12%).
heat energy 
Infrared radiation carries heat energy, which increases the temperature of the atmosphere.
infrared radiation 
The Earth’s surface reflects infrared radiation, part of which is retained in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases and clouds.
absorption by Earth surface 
About 50% of solar radiation is absorbed by the Earth’s surface.
absorption by clouds 
About 25% of solar radiation is absorbed by clouds.
absorbed solar radiation 
A portion of solar radiation is converted into thermal energy by gaseous constituents in the atmosphere, in the clouds and on the Earth’s surface.
solar radiation 
All the electromagnetic waves emitted by the Sun.